Qwen3-VL Inference
Qwen3-VL, PyTorch, LoRA, DeepStack, M-RoPE
On this page
1 Qwen3-VL Architecture
The Qwen3-VL model is a multi-modal large language model that integrates vision and language tasks. The architecture consists of:
- Vision Encoder
- MLP-based Vision-Language Merger
- Large Language Model backbone
The overall architecture is illustrated below:
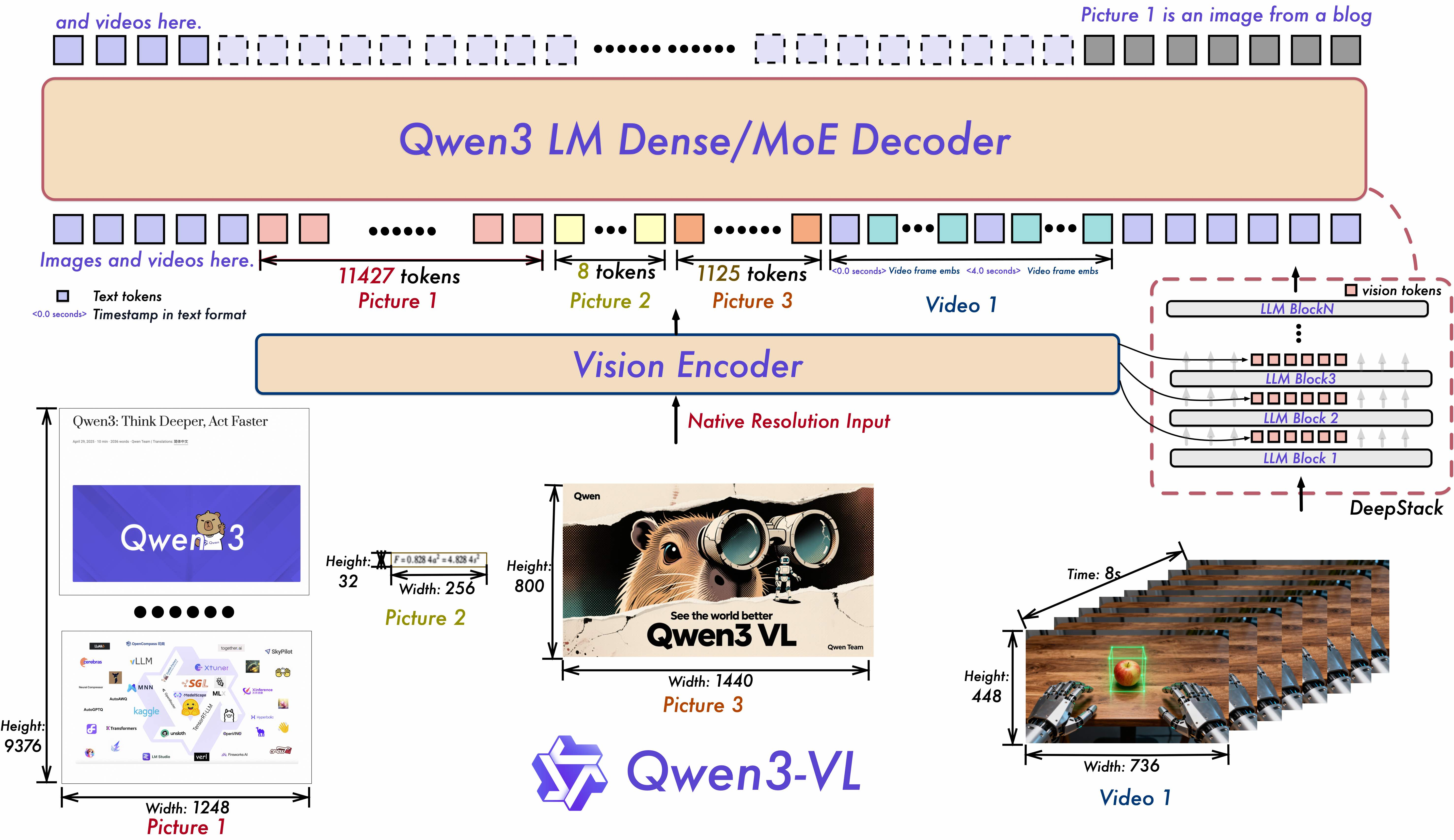
1.1 Image Input Processing
1.2 Vision Encoder
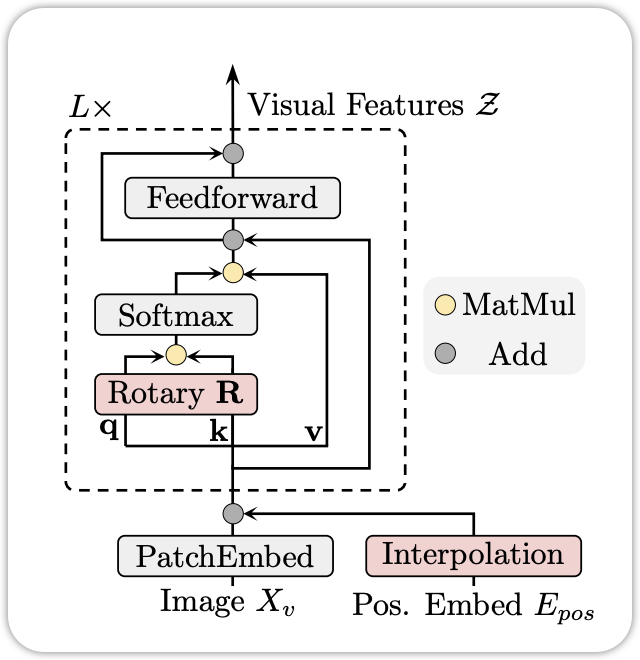
We utilize the SigLIP-2 architecture as our vision encoder and continue training it with dynamic input resolutions, initialized from official pretrained checkpoints. To accommodate dynamic resolutions effectively, we employ 2D-RoPE and interpolate absolute position embeddings based on input size, following the methodology of CoMP. Qwen3-VL Technical Report (Bai et al. 2025), P3
The vision encoder is the SigLip-2 architecture (Tschannen et al. 2025). As mentioned in the Qwen3-VL technical report (Bai et al. 2025), the weight is loaded from the SigLip-2 pretrained checkpoint, but with the continuous training to fit the dynamic input resolutions. One of the key techniques is change the position encoding. It use:
- 2D-RoPE (Rotary Position Embedding)(Su et al. 2023) to replace the original position encoding in ViT.
- Interpolate the absolute position embeddings based on input size.
1.2.1 2D RoPE
The 2D RoPe is an extension of the original RoPE (Su et al. 2023) to 2D inputs. The original RoPE is designed for 1D sequences, such as text. It encodes the position information by rotating the query and key vectors in the self-attention mechanism. The 2D RoPE extends this idea to 2D inputs, such as images. It encodes the position information by rotating the query and key vectors in both height and width dimensions. The mathematical formulation of 2D RoPE is as follows:
\[ \text{RoPE}_{2D}(Q, K, pos_h, pos_w) = Q \cdot R(pos_h) \cdot R(pos_w), K \cdot R(pos_h) \cdot R(pos_w) \tag{1}\]
where \(R(pos_h)\) and \(R(pos_w)\) are the rotation matrices for height and width positions, respectively. By applying 2D RoPE, the model can effectively capture the spatial relationships in images, which is crucial for vision tasks.
1.2.2 Position Interpolation
In addition to 2D RoPE, the Qwen3-VL model also uses position interpolation to handle dynamic input resolutions. The original ViT model uses absolute position embeddings, which are fixed for a specific input size. To accommodate dynamic input sizes, the Qwen3-VL model interpolates the absolute position embeddings based on the input size. The interpolation is done using bilinear interpolation, which allows the model to adapt to different input sizes without losing the positional information. The mathematical formulation of position interpolation is as follows:
\[ PE_{interp}(x, y) = \text{BilinearInterpolate}(PE, x, y) \tag{2}\]
where \(PE\) is the original position embedding matrix, and \((x, y)\) are the coordinates in the interpolated space. By using position interpolation, the model can effectively handle images of varying sizes while maintaining the positional information necessary for accurate vision tasks.
\[ \mathbf{R}_{x,y} = \left(\begin{array}{cc:cc} \cos x\theta & -\sin x\theta & 0 & 0 \\ \sin x\theta & \cos x\theta & 0 & 0 \\ \hdashline 0 & 0 & \cos y\theta & -\sin y\theta \\ 0 & 0 & \sin y\theta & \cos y\theta \end{array} \right) \tag{3}\]
where \(x\) and \(y\) are the position indices in height and width dimensions, respectively, and \(\theta\) is a predefined angle.
1.2.3 Patch Merger
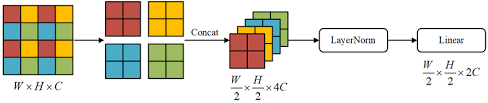
However, unlike other patch merger such as the one in Swin Transformer (Liu et al. 2021), the Patch Merger in Qwen3-VL is implemented as a linear layer that projects the concatenated patch embeddings into a lower-dimensional space. The adjcant patch embeddings are processed during the pre-processing step, and the Patch Merger layer simply reduces the dimensionality of the concatenated embeddings. Wewill see more
1.3 Vision Language Fusion
1.3.1 DeepStack
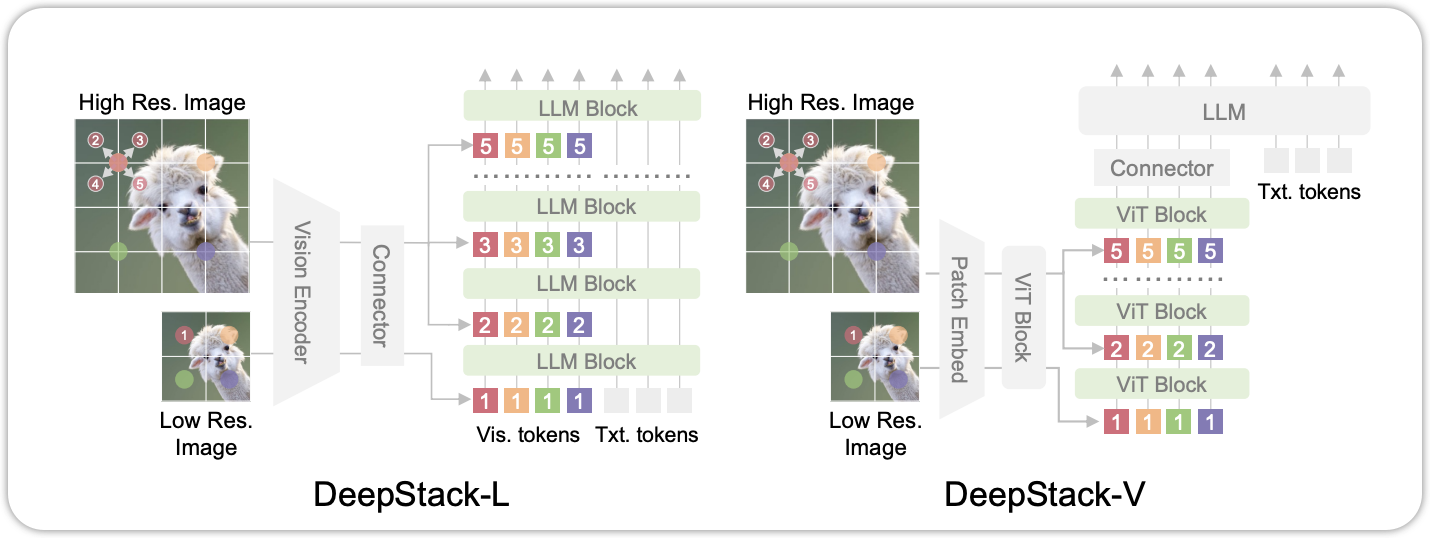
The DeepStack module is designed to effectively merge visual and textual information. It consists of multiple layers of cross-attention and feed-forward networks. The cross-attention mechanism allows the model to attend to relevant visual features based on the textual input, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the multi-modal data. The feed-forward networks further process the combined features to enhance their representation.