01: Attention is all you need (Transformer )
On this page
- 1 Preliminary
- 2 Summary
- 3 Key Concepts
- 4 Q & A
- 5 Related resource & Further Reading
我们开始第一篇论文的学习: 《Attention is All You Need》 (Vaswani et al. 2023),也就是传说中的Transformer模型。Transformer模型的提出,彻底改变了自然语言处理(NLP)以及更广泛的领域。该架构完全基于注意力机制(Attention),不再依赖循环(RNN)或卷积(CNN),因此在训练时更易并行化、效率更高。Transformer 已成为众多前沿模型的基础,不仅在 NLP 中表现突出,也扩展到计算机视觉等领域。比如 ChatGPT、DeepSeek 等大语言模型(LLM)都以 Transformer 为核心架构。所以我们自然就把它当作我们第一篇文章的首选。
1 Preliminary
在开始学习Transformer之前,我们预习一下一些需要的知识,以便我们可以更好的理解这个模型
1.1 Softmax Function
1.2 Vector Similarity
简单回顾了一下这些数学知识,接下来,让我们来看看Transformer到底是个什么东西。 # Transformer Transformer 是 Google 在2017年提出的新的神经网络架构,它的提出主要是为了解决,
- 序列建模(Sequence Modeling)的效率问题:
- 在 Transformer 出现之前,主流方法是 RNN(循环神经网络)和 CNN(卷积神经网络)。
- RNN 需要按顺序逐步处理序列,无法并行化,训练和推理效率低下。
- CNN 虽然有一定的并行性,但捕捉长距离依赖需要堆叠很多层,计算开销大。
- 长距离依赖建模问题:
- RNN 在捕捉长距离依赖时容易出现梯度消失(Gradient Vanish) 或梯度爆炸(Gradient Explosion),导致模型难以学习远距离的信息。
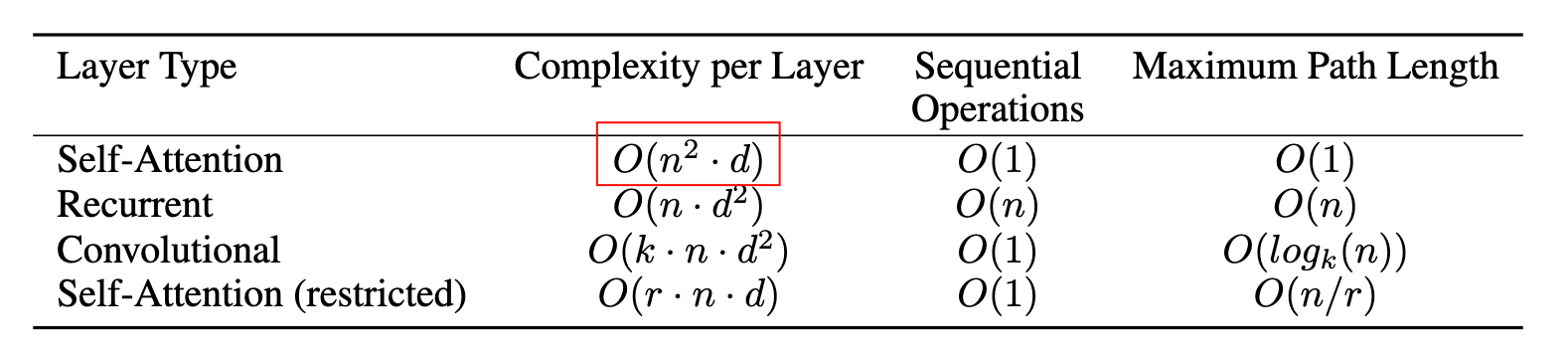
This inherently sequential nature precludes parallelization within training examples, which becomes critical at longer sequence lengths, as memory constraints limit batching across examples. … In these models, the number of operations required to relate signals from two arbitrary input or output positions grows in the distance between positions, linearly for ConvS2S and logarithmically for ByteNet. This makes it more difficult to learn dependencies between distant positions Attention is all you need, p.
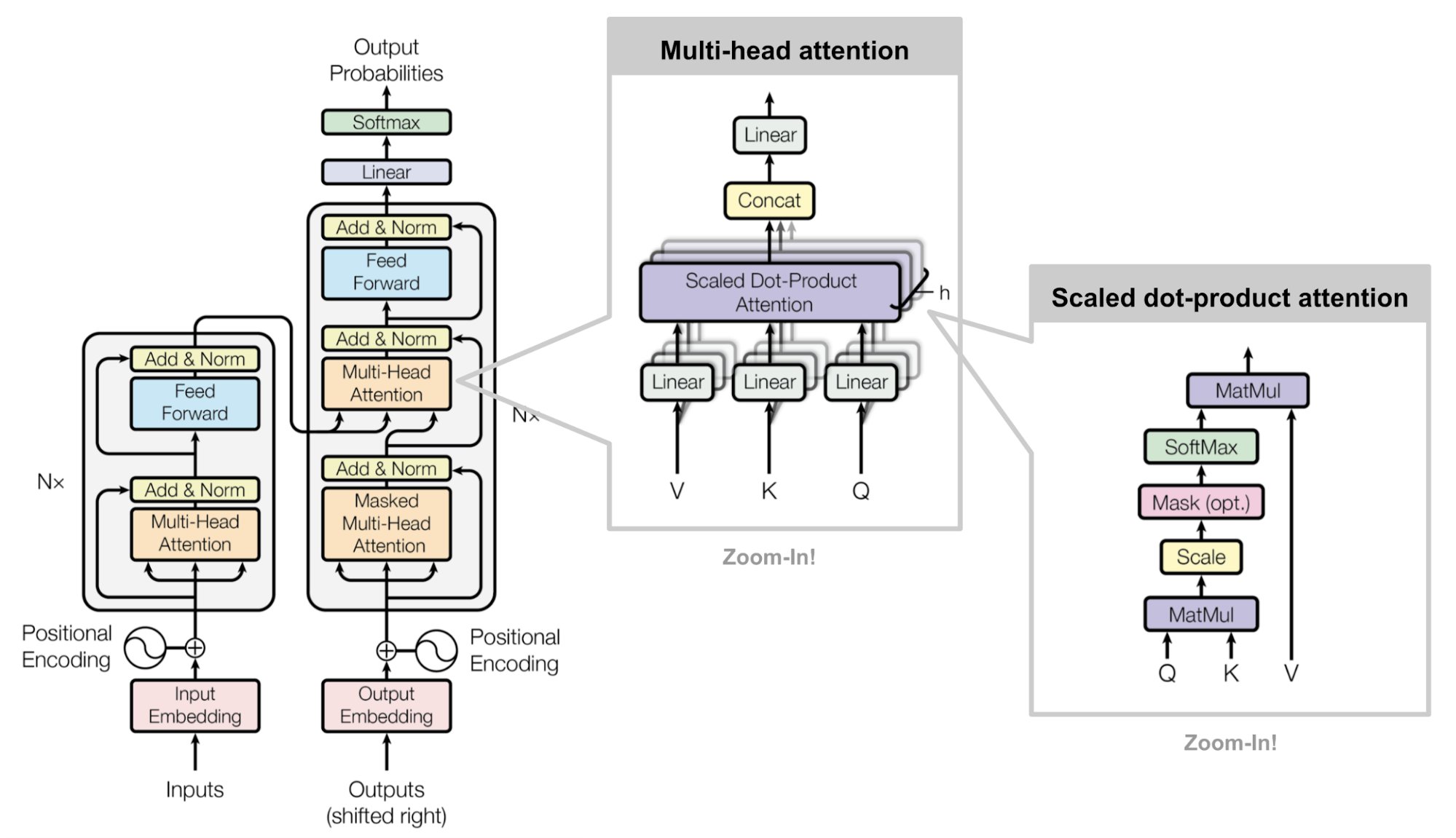
模型的基本架构如下图所示:
用代码显示就是:
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: ModelConfig):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(config)
self.decoder = Decoder(config)
self.output_layer = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.tgt_vocab_size)
...
def forward(self, original, target):
...接下来让我们从下至上,来深度解刨Transformer的模型结构分别是: 1. Word Embedding Layer 2. Position Embedding Layer 3. Attention Layer: 1. Self-Attention Layer 2. Cross-Attention Layer 4. Normalization Layer 5. Feed Forward Layer 6. Output Layer
1.3 Word Embedding Layer
Word Embedding 基本是所有语言模型的第一步,
1.4 Position Embedding Layer
\[ \begin{split} PE_{(pos, 2i)} & = \sin (pos / 10,000^{2i / d_{model}}) \\ PE_{(pos, 2i+1)} & = \cos (pos / 10,000^{2i+1 / d_{model}}) \end{split} \]
1.5 Attention Layer
1.5.1 Self-Attention Layer
1.5.2 Cross Attention Layer
\[ \begin{array}{|l|l|} \hline \textbf{Step} & \textbf{Time Complexity} \\ \hline QK^\top & \mathcal{O}(n^2 d) \\ \text{softmax}(QK^\top) & \mathcal{O}(n^2) \\ \text{attention} \times V & \mathcal{O}(n^2 d) \\ \hline \textbf{Total} & \mathcal{O}(n^2 d) \\ \hline \end{array} \]
1.6 Normalization Layer
Layer Normalization
1.7 Feed Forward Layer
\[ \text{FFN}(\mathrm{x}) = \underset{}{\max} (0, \mathrm{x} W_{1} + b_{1}) W_{2} + b_{2} \]
1.8 Residual Connection
\[ \mathbf{y} = \text{LayerNorm}(\mathbf{x} + \mathrm{Sublayer}(\mathbf{x})) \]
\[ \begin{split} \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial \mathbf{x}} &= \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial \mathbf{y}} \cdot \frac{\partial \mathbf{y}}{\partial \mathbf{x}} \\ &= \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial \mathbf{y}} \cdot \left( \mathbf{I} + \frac{\partial \mathrm{Sublayer}(\mathbf{x})}{\partial \mathbf{x}} \right) \\ &= \underbrace{\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial \mathbf{y}}}_{\text{straight path}} + \underbrace{\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial \mathbf{y}} \cdot \frac{\partial\,\mathrm{Sublayer}(\mathbf{x})}{\partial \mathbf{x}}}_{\text{through the sub-layer}} \end{split} \]
1.9 Output Layer
1.10 Others
当然,除了以上的一个部分,Transformer中还有几个值得一提的部分,不过处于篇幅的关系,在这里就不过多的赘述了,其中包括Tokenization等。
1.11 Experiment
1.12 Weight Initialization
1.12.1 Optimizer
Transformer的论文中,用的是Adam Optimizer,
对于不了的Adam的同学,也不用太担心,之后我们会有一系列的文章,专门介绍这些优化器的,包括Adam,AdamW,以及最近比较火的Moun
2 Summary
在这篇文章中,我们了解了什么是Transformer模型,以及它的重要组件,其中最重要的,也是最关键的,就是Attention机制,可以说Attention机制就是Transformer的核心,后续许多的工作,都是围绕着如何优化 Attention展开的。