11: Neural Discrete Representation Learning (VQ_VAE )
Representation Learning
Self Supervised Learning
一种通过离散化潜在表示并使用码本进行重构的生成模型,将连续表示转为离散符号,从而学习高质量、可组合的视觉表示并支持高效生成。
On this page
- 1 VQ_VAE
- 2 Summary
- 3 Key Concepts
- 4 Q & A
- 5 Related resource & Further Reading
- 6 Preliminary
- 7 VQ_VAE
- 8 Summary
- 9 Key Concepts
- 10 Q & A
- 11 Related resource & Further Reading
- 12 Preliminary
- 13 VQ_VAE
- 14 Summary
- 15 Key Concepts
- 16 Q & A
- 17 Related resource & Further Reading
- 18 VQ_VAE
- 19 Summary
- 20 Key Concepts
- 21 Q & A
- 22 Related resource & Further Reading
 # Preliminary
# Preliminary
1 VQ_VAE
1.1 Experiment
2 Summary
3 Key Concepts
4 Q & A
6 Preliminary
7 VQ_VAE
7.1 Experiment
8 Summary
9 Key Concepts
10 Q & A
12 Preliminary
12.1 Vector Quantization
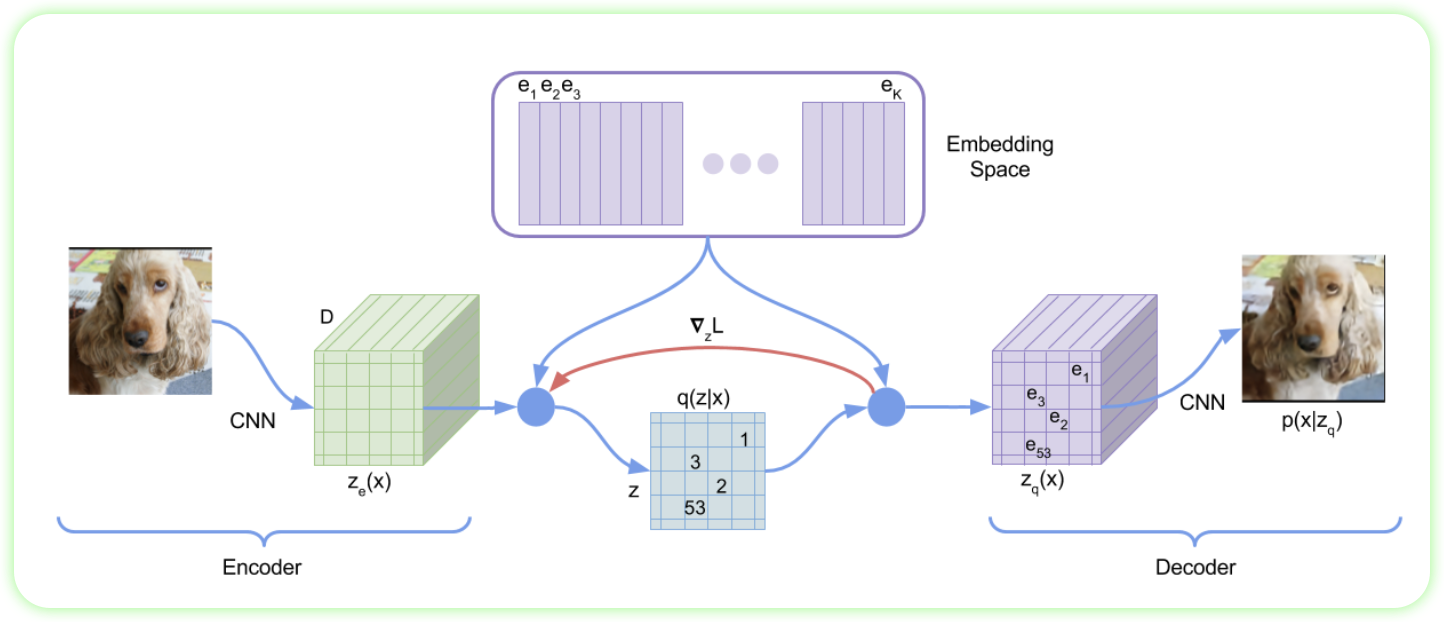
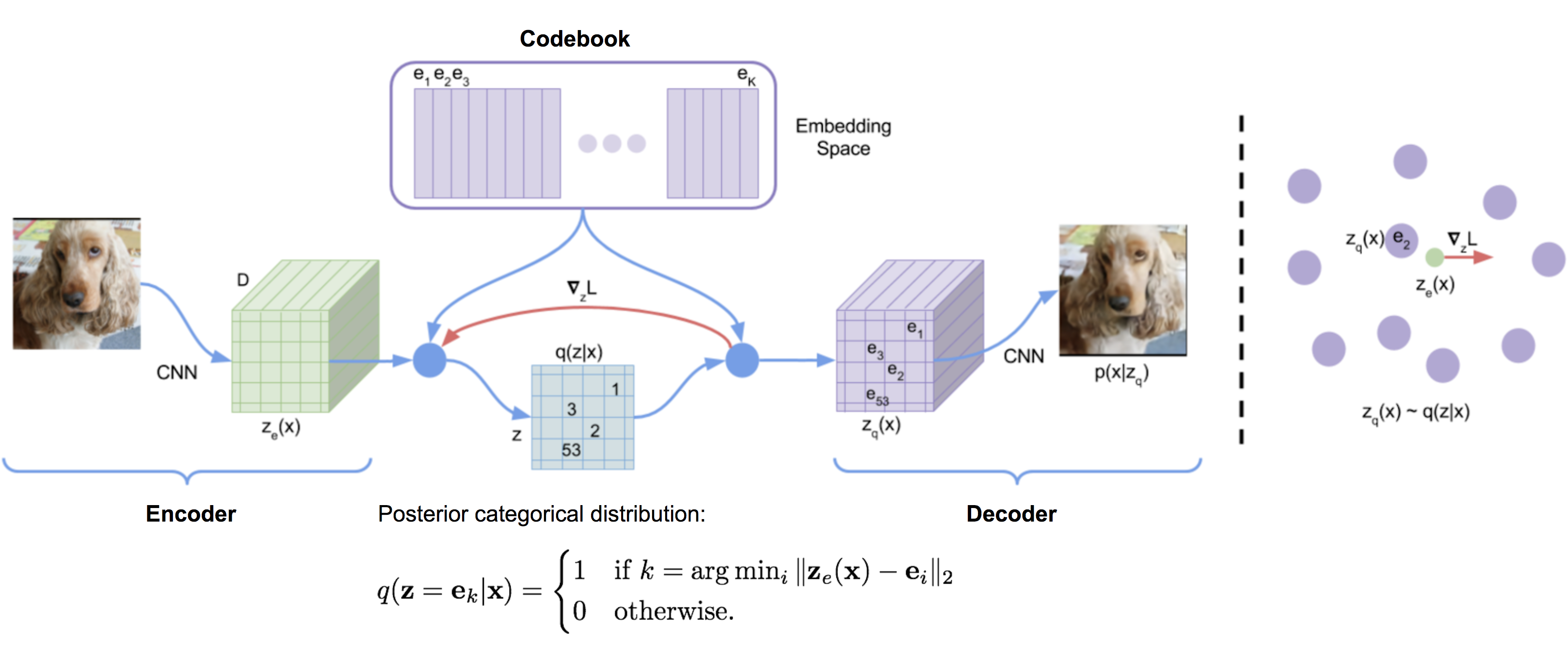
向量量化(Vector Quantization)是一种把连续的向量转换为离散的“索引” 的方法。通过这个索引,在字典(codebook)中找到一个与其最相近的一个向量,这个字典也叫做: - CodeBook - Embedding Table - Centroids 这时,每个向量就变成了一个离散的编号(Index) 用数学表达就是: 我们有: - A vector \(z \in \mathbb{R}^{d}\) - A codebook \(E \in \mathbb{R}^{K \times d}\), 其中 有 \(K\) 个索引
我们通过比较 \(z\) 和 \(K\) 个向量中,找到最近的一个向量
\[ \text{quantized}(z) = e_{k} \quad \text{where}\ k = \underset{j}{\operatorname{arg\min}} \|z - e_{j} \|^{2} \]
import torch
def quantize(embedding_table: torch.Tensor, z: torch.Tensor):
"""
embedding_table: (K, D)
z: (B, D)
"""
# (B, 1, D) - (1, K, D) → (B, K, D)
diff = z.unsqueeze(1) - embedding_table.unsqueeze(0)
# (B, K, D) -> (B, K)
distances = torch.linalg.norm(diff, dim=2)
# (B, K) -> (B,)
indices = distances.argmin(dim=1)
# Gather quantized embeddings → (B, D)
q = embedding_table[indices]
return q, indices
K, D = 512, 64
B = 8
codebook = torch.randn(K, D)
z = torch.randn(B, D)
q, idx = quantize(codebook, z)
assert q.shape == (B, D)
assert idx.shape == (B,)12.2 Straight Through Estimator
K, D = 512, 64
B = 8
embedding_table = torch.randn(K, D)
z_enc = torch.randn(B, D, requires_grad=True)
assert z_enc.grad is None
z_k, _ = quantize(embedding_table, z_enc)
# STE
z_k = z_enc + (z_k - z_enc).detach()
z_k.retain_grad()
loss = (z_k**2).mean()
loss.backward()
assert z_k.grad is not None
assert z_enc.grad is not None
assert torch.allclose(z_enc.grad, z_k.grad)13 VQ_VAE